НАФТАЛИН – НЕОБХОДИМЫЙ МЕТАБОЛИТ ДЛЯ ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ N-ФЕНИЛ-2-НАФТИЛАМИНА И ФТАЛАТОВ В РАСТЕНИЯХ ГОРОХА (PISUM SATIVUM L.)
УДК 633.358:577.73
Аннотация
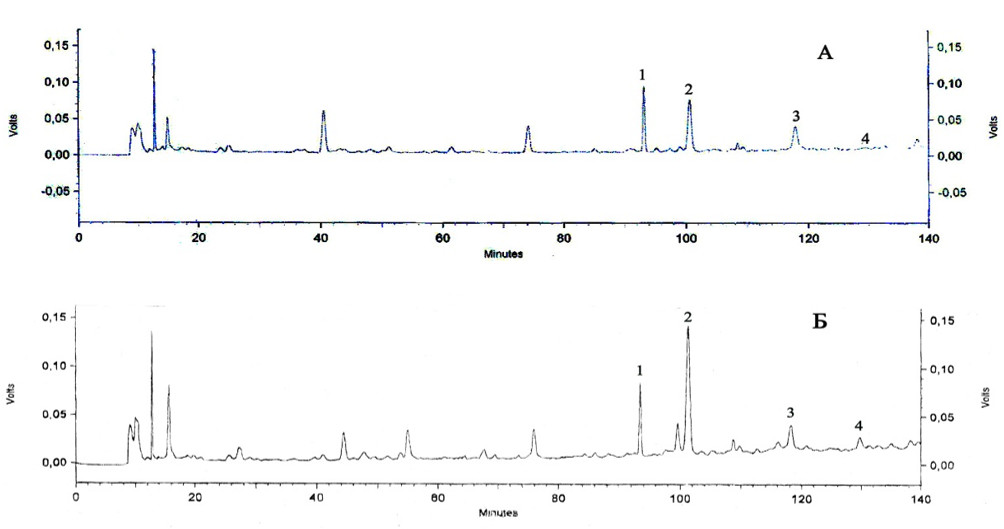
N-фенил-2-нафтиламин и фталаты – известные соединения, синтезируемые в химической промышленности. Их относят к веществам негативного действия на живые организмы. В то же время N-фенил-2-нафтиламин обнаружен в растениях, фталаты – в растениях и в бактериях. В настоящее время в научной литературе отсутствуют данные о путях синтеза N-фенил-2-нафтиламина и фталатов в растительных клетках. Наличие этих соединений ранее нами установлено в тканях корней и корневых экссудатов у бобовых культур. Цель представляемой работы – выяснить возможность использования нафталина растениями гороха посевного (Pisum sativum L.) в качестве предшественника синтеза N-фенил-2-нафтиламина и фталатов. Растительным объектом в экспериментах являлись корни этиолированных проростков гороха, росших в течение 24 ч на растворе 10-4 М нафталина. Контролем служили корни проростков, росших на воде. Из фиксированных 95%-ным этанолом корней последовательно при помощи 80% этанола и этилацетата получали экстракты, содержащие ароматические соединения. В их составе методом ВЭЖХ определили содержание N-фенил-2-нафтиламина, диэтил-, дибутил- и бис(2-этилгексил)фталатов, и методом спектрофотометрии по реакции с AlCl3, определяли общее содержание флавоноидов. Для подтверждения присутствия в экстрактах исследуемых соединений использовали их аутентичные образцы. Существенные увеличения, по сравнению с растениями контроля, содержания N-фенил-2-нафтиламина и фталатов в корнях при росте на растворе нафталина указывают на его использование растением гороха в качестве необходимого метаболита для биосинтеза вышеназванных соединений. При действии нафталина обнаружено отсутствие изменений в содержании флавоноидов.
Скачивания
Metrics
Литература
Slovar' organicheskikh soyedineniy [Dictionary of organic compounds], ed. I.N. Kheyl'bron, G.M. Benberi. Moscow, 1949, vol. 3, 977 p. (in Russ.).
Yu R., Li B.-G., Ye Q., Zhang G.-l. Natural Product Research, 2005, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 359–362.
Hauser R., Calafat A.M. Occup Environ Med., 2005, vol. 62, no. 11, pp. 806–818.
Mankidi R., Wiseman S., Ma H., Giesy J.P. Toxicology Letters, 2013, vol. 217 (1), pp. 50–58. DOI: 10/1016/j.toxlet2012.11.025.
Altenburger R., Braсk W., Greco W.R., Groot M., Jung K., Ovari A., Riedl J., Schwab K., Kữster E. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 40, no. 19, pp. 6163–6169.
Sultankhodzhayev M.N., Tadzhibayev M.M. Khimiya prirodnykh soyedineniy, 1976, vol. 12, no. 3, p. 406. (in Russ.).
Yevstratova R.I., Zapesochnaya G.G. Khimiya prirodnykh soyedineniy, 1977, no. 4, p. 582. (in Russ.).
Zhanayeva T.A., Krivoshchekova O.Ye., Semenov A.A., Minayeva V.G. Khimiya prirodnykh soyedineniy, 1989, vol. 25, no. 3, p. 377. (in Russ.).
Shi D.Y., Han L.J., Sun J., Wang Y., Yang Y.C., Shi J.G., Fan X. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2005, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 347–350.
Wu Z.B., Zhang S.H., Wu X.H., Cheng S.P., He F. Allelopathy Journal, 2007, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 327–338.
Enikeev A.G., Semenov A.A., Permyakov A.V., Sokolova N.A., Gamburg K.Z., Dudareva L.V. Prikladnaya bio-khimiya i mikrobiologiya, 2019, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 282–285. DOI: 10.1134/S0555109919020065. (in Russ.).
Shafikova T.N., Omelichkina Yu.V., Boyarkina S.V., Enikeev A.G., Maksimova L.A., Semenov A.A. Doklady Akad-emii nauk, 2019, vol. 484, no. 1, pp. 121–124. (in Russ.).
Makarova L.Ye., Smirnov V.I., Klyba L.V., Petrova I.G., Dudareva L.V. Prikladnaya biokhimiya i mikrobiologiya, 2012, vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 394–403. (in Russ.).
Makarova L.Ye., Morits A.S., Sokolova N.A., Petrova I.G., Semenov A.A., Dudareva L.V., Tret'yakova M.S., Si-dorov A.V. Prikladnaya biokhimiya i mikrobiologiya, 2020, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 165–173. DOI: 10.31857/S0555109920010122. (in Russ.).
Makarova L.Ye., Kapustina I.S., Morits A.S., Makarov S.S. Siberian Journal of Life Sciences and Agriculture, 2021, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 162–184. DOI: 10.12731/2658-6649-2021-13-2-162-184. (in Russ.).
Makarova L.Ye., Dudareva L.V., Petrova I.G., Vasil'yeva G.G. Prikladnaya biokhimiya i mikrobiologiya, 2016, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 217–222. DOI: 10.7868/S0555109916020094. (in Russ.).
Makarova L.Ye., Markova Yu.A., Morits A.S., Karepova M.S., Sidorov A.V., Sokolova N.A. Prikladnaya biokhimiya i mikrobiologiya, 2021, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 394–401. DOI: 10.31857/S0555109921040103. (in Russ.).
Kiyohara H., Nagao K., Nomi R. J. Gen. Microbiol., 1978, vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 69–75.
Barnsley E.A. J. Bacteriol., 1983, vol. 154, no. 1, pp. 113–117.
Seo J.S., Keum Y.-S., Li Q.X. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2009, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 278–309. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph6010278.
Puntus I.F., Filonov A.Ye., Akhmetov L.I., Karpov A.V., Boronin A.M. Mikrobiologiya, 2008, no. 1, pp. 11–20. (in Russ.).
Reddy P.M., Rendón-Anaya M., de los Dolores Soto del Río M., Khandual S. Dynamic Soil, Dynamic Plant, 2007, vol. 1(2), pp. 83–94.
Zhishen J., Mengcheng T., Jianming W. Food Chemistry, 1999, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 555–559.
Ma T., Teng Y., Christie P., Luo Y. Front Environ. Sci. Eng., 2015, vol. 9(2), pp. 250–268. DOI: 10.1007/s11783-014-0652-2.
Copyright (c) 2023 Химия растительного сырья

Это произведение доступно по лицензии Creative Commons «Attribution» («Атрибуция») 4.0 Всемирная.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Авторы, которые публикуются в данном журнале, соглашаются со следующими условиями:
1. Авторы сохраняют за собой авторские права на работу и передают журналу право первой публикации вместе с работой, одновременно лицензируя ее на условиях Creative Commons Attribution License, которая позволяет другим распространять данную работу с обязательным указанием авторства данной работы и ссылкой на оригинальную публикацию в этом журнале.
2. Авторы сохраняют право заключать отдельные, дополнительные контрактные соглашения на неэксклюзивное распространение версии работы, опубликованной этим журналом (например, разместить ее в университетском хранилище или опубликовать ее в книге), со ссылкой на оригинальную публикацию в этом журнале.
3. Авторам разрешается размещать их работу в сети Интернет (например, в университетском хранилище или на их персональном веб-сайте) до и во время процесса рассмотрения ее данным журналом, так как это может привести к продуктивному обсуждению, а также к большему количеству ссылок на данную опубликованную работу.











