MICROELEMENT COMPOSITION OF PATRINIA SCABIOSIFOLIA AND PATRINIA RUPESTRIS
UDC 631.81.033
Abstract
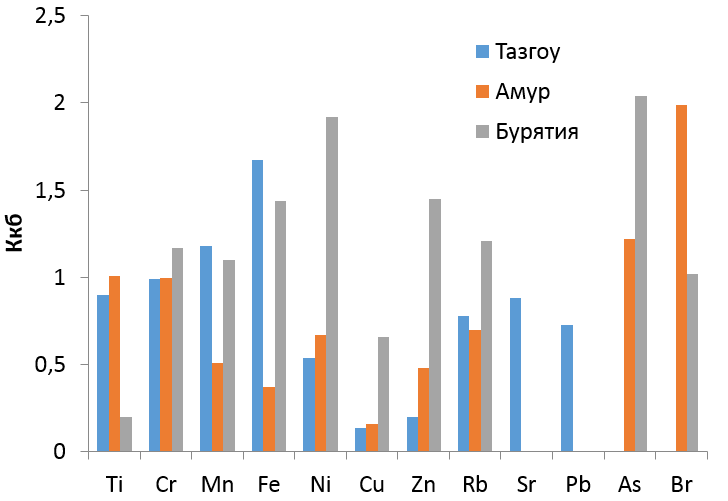
Anthropogenic activity leads to an increased content of trace elements in environmental resources: air, water, land and biota. The accumulation of elements is influenced by the properties of the element, the characteristics of the environment, and the factors of the host organism. This necessitates monitoring of plant materials, especially in regions with a significant raw material base of medicinal plants, but actively exposed to anthropogenic impact, which currently includes the Russian Far East. The article presents the results of studying the elemental composition of plant raw materials of Patrinia rupestris and Patrinia scabiosifolia. It has been established that P. rupestris raw material contains 11-12 elements, P. scabiosifolia raw material contains 11-14 elements, depending on the habitat, 8 of them are essential, 4 are conditionally essential. The homogeneous elemental composition of the grass and roots of P. rupestris and P. scabiosifolia reflects the genetic closeness of the studied species. For most elements, both species exhibit the properties of moderate accumulation and strong capture. Mn, Cr, Ni maintain a constant concentration throughout the range, both for P. rupestris and P. scabiosifolia. Foliar uptake of Co, Br for both species, and Ba for P. rupestris was noted. For P. rupestris and P. scabiosifolia, an acropetal type of element accumulation is noted in Primorye; in the mainland areas of the ranges, a reverse strategy of element accumulation is observed.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Ufimtseva M.D., Terekhina N.V. Vestnik SPbGU. Nauki o Zemle, 2017, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 209–217. (in Russ.).
Kiku P.F., Gel'tser B.I. Ekologicheskiye problemy zdorov'ya. [Ecological health problems]. Vladivostok, 2004, 226 p. (in Russ.).
Mikroelementy v okruzhayushchey srede. [Microelements in the environment], ed. M.N.V. Prasad, K.S. Sajwan, R. Naid. Moscow, 2009, 816 p. (in Russ.).
Il'in V.B., Syso A.I. Mikroelementy i tyazhelyye metally v pochvakh i rasteniyakh Novosibirskoy oblasti. [Microele-ments and heavy metals in soils and plants of the Novosibirsk region]. Novosibirsk, 2001, 229 p. (in Russ.).
Bulaev V.M. Sovremennaya fitoterapiya. [Modern herbal medicine]. Moscow, 2011, 144 p. (in Russ.).
Bezdelev A.B., Bezdeleva T.A. Zhiznennyye formy semennykh rasteniy rossiyskogo Dal'nego Vostoka. [Life forms of seed plants of the Russian Far East]. Vladivostok, 2006, 296 p. (in Russ.).
He X., Luan F., Zhao Z., Ning N., Li M., Jin L., Chang Y., Zhang Q., Wu N., Huang L. The American Journal of Chi-nese Medicine, 2017, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 637–666. DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X17500379.
Li Z., Tang Y., Zhu S., Li D., Han X., Gu G., Xing N., Ren J., Guo Z., Jiao W., Yan L., Xu Z., Zhang W. Oncology Reports, 2018, vol. 39, pp. 764–772. DOI: 10.3892/or.2017.6139.
Zhang M.Y., Sun G.D., Shen A.L., Liu L.Y., Ding J.Z., Peng J. Oncology Reports, 2015, vol. 33, pp. 856–860. DOI: 10.3892/or.2014.3663.
Sheng L., Yang Y., Zhang Y., Li N. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2019, vol. 236, pp. 129–135. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.005.
Meng L., Chen S., Zhou L., Liu Z., Li S., Kang W. Current Pharmacology Reports, 2020, vol. 6, pp. 380–414. DOI: 10.1007/s40495-020-00240-7.
Lei, J.C., Yang C.X., Yang Y., Zhang W., Yu J.Q. Journal of functional foods, 2015, vol. 16, pp. 289–294. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.04.037.
Afanas'yeva L.V., Ayushina T.A. Khimiya Rastitel'nogo Syr'ya, 2018, no. 3, pp. 123–128. DOI: 10.14258/jcprm.2018033740. (in Russ.).
Predel'no dopustimyye kontsentratsii (PDK) khimicheskikh veshchestv v pochve: Gigiyenicheskiye normativy. [Maxi-mum permissible concentrations (MAC) of chemicals in soil: Hygienic standards]. Moscow, 2006, 15 p. (in Russ.).
Golov V.I. Krugovorot sery i mikroelementov v osnovnykh agroekosistemakh Dal'nego Vostoka. [Cycle of sulfur and microelements in the main agroecosystems of the Far East]. Vladivostok, 2004, 315 p. (in Russ.).
Tutel'yan V.A. Khimicheskiy sostav i kaloriynost' rossiyskikh produktov pitaniya. [Chemical composition and calorie content of Russian food products]. Moscow, 2012, 284 p. (in Russ.).
Titov A.F., Kaznina N.M., Talanova V.V. Tyazhelyye metally i rasteniya. [Heavy metals and plants]. Petrozavodsk, 2014, 192 p. (in Russ.).
SanPiN 2.3.2.1078-01. Sanitarno-epidemiologicheskiye pravila i normativy. Gigiyenicheskiye trebovaniya bezopasnosti i pishchevoy tsennosti pishchevykh produktov. [SanPiN 2.3.2.1078-01. Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regula-tions. Hygienic requirements for food safety and nutritional value]. Moscow, 2002, 145 p. (in Russ.).
Kopylov N.I., Kaminsky Yu.D. Mysh'yak. [Arsenic]. Novosibirsk, 2004, 367 p. (in Russ.).
Copyright (c) 2023 chemistry of plant raw material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











