EFFECT OF HIGH-FREQUENCY ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD ON THE MUTAROTATION OF AQUEOUS SOLU-TIONS OF GLUCOSE AND FRUCTOSE
Abstract
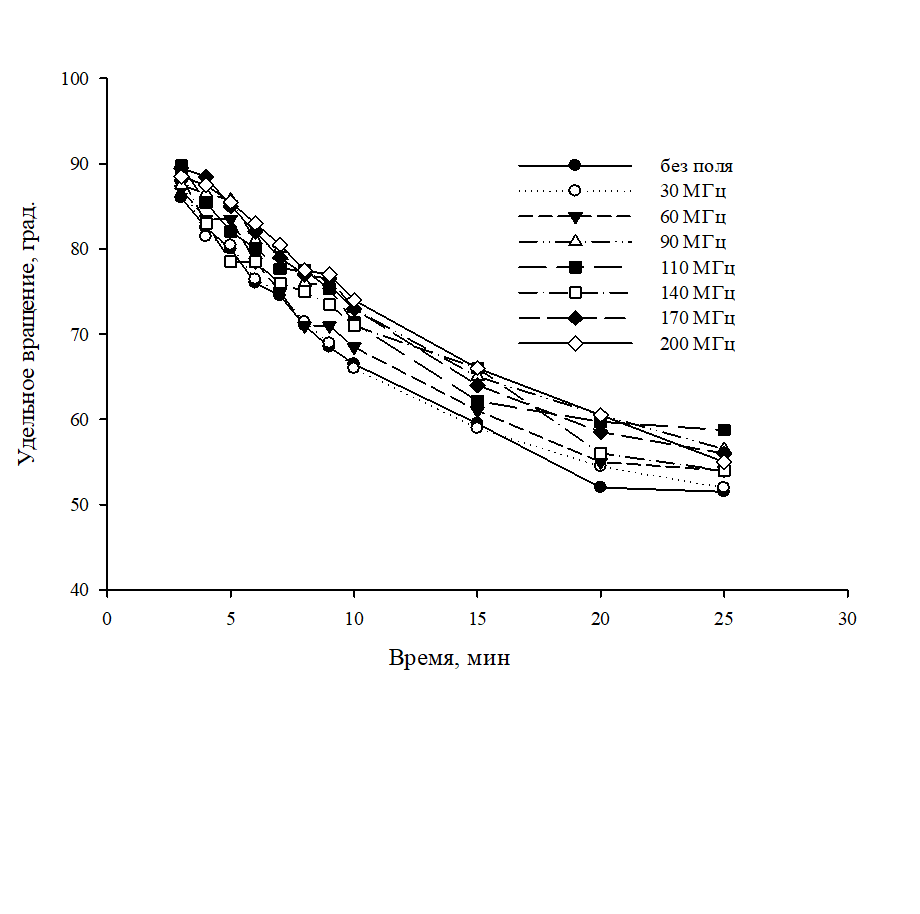
The indirect influence of the high-frequency electromagnetic field of the 30–200 MHz low power range on the reaction rate of the mutation of D-glucose solutions and on the equilibrium in D-fructose and D-glucose solutions was studied. Solutions were prepared using both deionized water and water exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Control of the process of mutarotation was carried out polarimetrically. To assess the effectiveness of field exposure, the effective constants of the reaction rate of mutarotation were calculated. It has been established that the rate of mutarotation of D-glucose solutions non-linearly decreases with increasing frequency of the electromagnetic field. The effect of pretreatment of the solvent by an electromagnetic field on the equilibrium in solutions of fructose and glucose, which have been subjected to field exposure, has been studied. The observation was carried out for 30 days. It was found that the equilibrium specific rotation in the fructose solution as a result of the influence of the electromagnetic field shifts towards negative values, and in the case of glucose solution it does not change. An explanation of the results obtained is proposed, which is based on the assumption of a change in the structural organization of the solvent - water as a result of the high-frequency electromagnetic field, which can significantly change the hydration interactions of the reaction participants: carbohydrates and hydrogen ions.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Kochetkov N.K., Bochkov A.F., Dmitriyev A.B., Usov A.I., Chizhov O.S., Shibayev V.N. Khimiya uglevodov. [Chemistry of carbohydrates]. Moscow, 1966, 672 p. (in Russ.).
Abrosimov V.K., Agafonov A.V., Antini Ye.V. et al. Biologicheski aktivnyye veshchestva v rastvore. Struktura. Ter-modinamika. Reaktsionnaya sposobnost'. [Biologically active substances in solution. Structure. Thermodynamics. Reac-tivity]. Moscow, 2001, 408 p. (in Russ.).
Shmid R., Sapunov V.N. Neformal'naya kinetika. V poiskakh putey khimicheskikh reaktsiy. [Informal kinetics. In search of chemical reactions]. Moscow, 1985, 264 p. (in Russ.).
Ashmor P. Kataliz i ingibirovaniye. [Catalysis and inhibition]. Moscow, 1966, 500 p. (in Russ.).
Isbell H.S., Pigman W. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem., 1969, vol. 24, pp. 14–65.
Shipunov B.P., Timiryazev A.V., Kondratova Ye.V. Butlerovskiye soobshcheniya, 2011, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 105–109. (in Russ.).
Han H.B., Guo B., Chai F. Manufacturing Engineering and Automation II, 2012, vol. 591–593, pp. 2608–2609. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.591-593.2607.
Stillinger F.H., David C.W. J. Chem. Phys., 1978, vol. 69, no. 4, pp. 1473 – 1484.
Miljkovic M. Carbohydrates: Synthesis, Mechanisms and Stereoelectronic effects. New York: Springer, 2009, 543 p. DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-92265-2.
Barkovskiy V.F. Fiziko-khimicheskiye metody analiza. [Physico-chemical methods of analysis]. Moscow, 1972, 344 p. (in Russ.).
Riznichenko G.Yu., Plyusnina T.Yu. Zhurnal fizicheskoy khimii, 1997, vol. 71, no. 12, pp. 2264–2269. (in Russ.).
Fokin A.V., Kaznacheyev V.P. Elektromagnitnyye polya v biosfere. Biologicheskoye deystviye elektromagnitnykh poley. [Electromagnetic fields in the biosphere. The biological effect of electromagnetic fields]. Moscow, 1984, vol. 2, 326 p. (in Russ.).
Mokrousov G.M., Gorlenko N.P., Chemodanov D.I. Fiziko-khimicheskiye protsessy v magnitnom pole. [Physicochem-ical processes in a magnetic field]. Tomsk, 1988, 128 p. (in Russ.).
Dukhanin V.S. Issledovaniye vliyaniya magnitnogo polya na gidratatsiyu ionov v rastvorakh elektrolitov i na skorost' nekotorykh khimicheskikh reaktsiy: avtoref. dis…. kand. khim. nauk. [Investigation of the effect of a magnetic field on ion hydration in electrolyte solutions and on the rate of some chemical reactions: abstract. dis .... Cand. Chem. sciences]. Moscow, 1973, 21 p. (in Russ.).
Loginova O.N., Shipunov B.P., Sichkareva O.G., Safronova N.V. Izvestiya Altayskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta, 2010, pp. 163–166. (in Russ.).
Shatalov V.M. Biofizika, 2012, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1034–1040. (in Russ.).
Polevik N.D. Biofizika, 2013, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 697–703. (in Russ.).
Stas I.E., Shipunov B.P., Ivonina T.S. Electroanalysis, 2005, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 794–799. DOI: 10.1002/elan.200303146.
Shipunov B.P. Strukturnaya organizatsiya i gomogennoye ravnovesiye v vodnykh rastvorakh. Vliyaniye elektromag-nitnogo polya. [Structural organization and homogeneous equilibrium in aqueous solutions. The influence of an electro-magnetic field]. Saarbrücken: LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, 2014, 104 p. (in Russ.).
GOST R 8.736-2011 Gosudarstvennaya sistema obespecheniya yedinstva izmereniy (GSI). Izmereniya pryamyye mno-gokratnyye. Metody obrabotki rezul'tatov izmereniy. Osnovnyye polozheniya. [GOST R 8.736-2011 State system for ensuring the uniformity of measurements (GSI). The measurements are direct multiple. Methods for processing meas-urement results. The main provisions]. Moscow, 2013, 20 p. (in Russ.).
Fizer L., Fizer M. Organicheskaya khimiya. Uglublennyy kurs. [Organic chemistry. Advanced course]. Moscow, 1970, vol. II, 800 p. (in Russ.).
Copyright (c) 2019 Khimiia rastitel'nogo syr'ia (Chemistry of plant raw material)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











