ECDYSTEROIDS OF SILENE ITALICA: GLYCOSIDIC AND NONGLYCOSIDIC COMPONENTS AND HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS PROFILE
UDC 582.669.26 : 547.92
Abstract
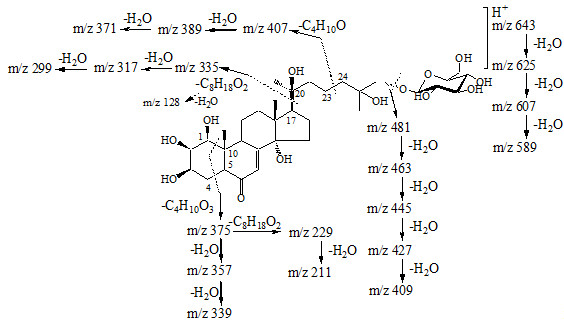
Silene italica (L.) Pers. is a species of Caryophyllaceae family which introduced samples contain ecdysteroids that was previously shown (Meng et al., 2001). In this paper, the composition of ecdysteroids of wild-growing S. italica was shown. Using high performance chromatography with diode-array detection and electrospray ionization mass-spectrometry detection (HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS) twenty-two compounds assigned to the ecdysteroid group. The non-glycoside components of S. italica were included twelve compounds and integristerone A, 26-hydroxyintegristerone A, 22-deoxyintegristerone A, 2-deoxyintegristerone A, and 2-deoxypolypodine B were identified for the first time. Ten compounds were characterized as ecdysteroid monoglycosides containing hexose fragment as a carbohydrate part. Trer were derivatives of 20-hydroxyecdysone, polypodine B, ecdysone and 2-deoxypolypodine B. For the first time, the presence of 22-deoxyintegristerone A hexoside non-detected in plant objects was found. Comparative analysis of the ecdysteroids composition of S. italica and well studied species S. italica spp. nemoralis (Báthori et al., 2000, 2002, 2004; Pongrácz et al., 2003; Simon et al., 2002) indicates their proximity. Quantitative analysis of five ecdysteroid content in the organs of S. italica showed that they were unevenly distributed in the plant. The concentration of 20-hydroxyecdysone was 0.10–32.12 mg/g and the total ecdysteroids content was 0.10–40.92 mg/g of dry plant weight. In general, it should be noted that the ability to produce and accumulate ecdysteroids was also observed for the wild samples of S. italica, which cultural samples was noted as ecdysteroid concentrator.
Downloads
Metrics
References
2. Флора СССР. Т. VI. Ред. В.Л. Комаров. Москва, Ленинград: АН СССР, 1936. С. 577–691.
3. Meng Y., Whiting P., Zibareva L., Bertho G., Girault J.-P., Lafont R., Dinan L. Identification and quantitative analysis of the phytoecdysteroids in Silene species (Caryophyllaceae) by high-performance liquid chromatography: Novel ecdysteroids from S. pseudotites // J. Chromatogr. A. 2001. Vol. 935. No 1–2. P. 309–319. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00893-7.
4. Báthori M., Pongrácz Z., Omacht R., Máthé I. Preparative scale purification of shidasterone, 2-deoxy-polypodine B and 9α,20-dihydroxyecdysone from Silene italica ssp. nemoralis // J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2004. Vol. 42. No 5. P. 275–279. DOI: 10.1093/chromsci/42.5.275.
5. Báthori M., Pongrácz Z., Tóth G., Simon A., Kandra L., Kele Z., Ohmacht R. Isolation of a new member of the ecdysteroid glycoside family: 2-deoxy-20-hydroxyecdysone 22-O-β-D-glucopyranoside // J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2002. Vol. 40. No 7. P. 409–415. DOI: 10.1093/chromsci/40.7.409.
6. Simon A., Pongrácz Z., Tóth G., Mák M., Máthé I., Báthori M. A new ecdysteroid with unique 9β-OH and four other ecdysteroids from Silene italica ssp. nemoralis // Steroids. 2004. Vol. 69. No 6. P. 389–394. DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2004.03.009.
7. Báthori M., Kalász H., Pongrácz Z., Máthé I., Kálmán A., Argay G. 5-Alpha- and 5-beta-2-deoxyintegristerone A, a 5-alpha and 5-beta isomer pair of ecdysteroids isolated from the Silene genus // Biomed. Chrom. 2002. Vol. 16. No 6. P. 373–378. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.168.
8. Báthori M., Blunden G., Kalász H. Two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of plant ecdysteroids // Chromatographia. 2000. Vol. 52. No 11–12. P. 815–817. DOI: 10.1007/BF02491010.
9. Pongrácz Z., Báthori M., Tóth G., Simon A., Mák M., Máthé I. 9α,20-Dihydroxyecdysone, a new natural ecdysteroid from Silene italica ssp. nemoralis // J. Nat. Prod. 2003. Vol. 66. No 3. P. 450–451. DOI: 10.1021/np0205194.
10. Zibareva L. Distribution and levels of phytoecdysteroids in plants of the genus Silene during development // Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2000. Vol. 43. No 1. P. 1–8. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(200001)43:1<1::AID-ARCH1>3.0.CO;2-D.
11. Zengin G., Mahomoodally M.F., Aktumsek A., Ceylan R., Uysal S., Mocan A., Yilmaz M.A., Picot-Allain C.M.N., Ćirić A., Glamočlija J., Soković M. Functional constituents of six wild edible Silene species: A focus on their phytochemical profiles and bioactive properties // Food Biosci. 2018. Vol. 23. P. 75–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.fbio.2018.03.010.
12. Jürgens A., Witt T., Gottsberger G. Flower scent composition in night-flowering Silene species (Сaryophyllaceae) // Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2002. Vol. 30. No 5. P. 383–397. DOI: 10.1016/S0305-1978(01)00106-5.
13. Olennikov D.N., Kashchenko N.I. Phytoecdysteroids of Silene jenisseensis // Chem. Nat. Comp. 2017. Vol. 53. No 6. P. 1199–1201. DOI: 10.1007/s10600-017-2239-1.
14. Olennikov D.N. Ecdysteroids, flavonoids and phenylpropanoids of Silene nutans // Chem. Nat. Comp. 2019. Vol. 55. No 1. P. 107–110. DOI: 10.1009/s11720-012-2242-4.
15. Stevens J.F., Reed R.L., Morré J.T. Characterization of phytoecdysteroid glycosides in Meadowfoam (Limnanthes alba) seed meal by positive and negative ion LC-MS/MS // J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008. Vol. 56. No 11. P. 3945–3952. DOI: 10.1021/jf800211k.
16. Girault J.-P., Bathori M., Varga E., Szendrei K., Lafont R. Isolation and identification of new ecdysteroids from the Caryophyllaceae // J. Nat. Prod. 1990. Vol. 53. No 2. P. 279–293. DOI: 10.1021/np50068a002.
17. Jayasinghe L., Mallika Kumarihamy B.M., Suranga Arundathie B.G., Dissanayake L., Hara N., Fujimoto Y. A new ecdysteroid, 2-deoxy-5β,20-dihydroxyecdysone from the fruits of Diploclisia glaucescens // Steroids. 2003. Vol. 68. No 5. P. 447–450. DOI: 10.1016/S0039-128X(03)00046-1.
18. Zibareva L., Yeriomina V.I., Munkhjargal N., Girault J.-P., Dinan L., Lafont R. The phytoecdysteroid profiles of 7 species of Silene (Caryophyllaceae) // Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2009. Vol. 72. No 4. P. 234–248. DOI: 10.1002/arch.20331.
19. Buděšínský M., Vokáč K., Harmatha J., Cvačka J. Additional minor ecdysteroid components of Leuzea carthamoides // Steroids. 2008. Vol. 73. No 5. P. 502–514. DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.021.
20. Зибарева Л., Волкова О., Морозов С., Черняк Е. Фитоэкдистероиды корней Silene fridvalszkyana // Химия растит. сырья. 2016. № 1. С. 71–75. DOI: 10.14258/jcprm.2017011416.
21. Alison B., Whiting P., Sarker S.D., Dinan L., Underwood E., Šik V., Rees H.H. 20-Hydroxyecdysone 2-β-D-glucopyranoside from the seeds of Xerophyllum tenax // Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997. Vol. 25. No 3. P. 255–261. DOI: 10.1016/S0305-1978(97)00003-3.
22. Sarker S.D., Savchenko T., Šik V., Rees H.H., Dinan L. 20-Hydroxyecdysone and its glucosides from Trisetum flavescens // Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1998. Vol. 26. No 1. P. 135–137. DOI: 10.1016/S0305-1978(97)00087-2.
23. Zhang Z., Yang W., Fan C., Zhao H., Huang X., Wang Y., Ye W. New ecdysteroid and ecdysteroid glycosides from the roots of Serratula chinensis // J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017. Vol. 19. No 3. P. 208–214. DOI: 10.1080/10286020.2016.1209492.
24. Saatov Z., Abdullaev N.D., Gorovits M.B., Abubakirov N.K. Phytoecdysteroids of plants of the genus Silene. VII. Sileneoside D – ecdysterone 3-O-α-D-galactopyranoside from Silene brahuica // Chem. Nat. Comp. 1984. Vol. 20. No 6. P. 700–703. DOI: 10.1007/BF00580027.
25. Saatov Z., Gorovits M.B., Abdullaev N.D., Yasmanov B.Z., Abubakirov N.K. Phytoecdysteroids of plants of the genus Silene. III. Sileneoside A – a new glycosidic ecdysteroid of Silene brachuica // Chem. Nat. Comp. 1981. Vol. 17. No 6. P. 534–539. DOI: 10.1007/BF00574372.
26. Simon A., Ványolós A., Béni Z., Dékány M., Tóth G., Báthori M. Ecdysteroids from Polypodium vulgare L. // Steroids. 2011. Vol. 76. No 13. P. 1419–1424. DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2011.07.007.
27. Kißmer B., Wichtl M. Ecdysone aus Wurzeln und Samen von Helleborus-Arten // Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim). 1987. Vol. 320. P. 541–546. DOI: 10.1002/ardp.19873200611.
28. Jadhav A.N., Pawar R.S., Avula B., Khan I.A. Ecdysteroid glycosides from Sida rhombifolia L. // Chem. Biodiv. 2007. Vol. 4. No 9. P. 2225–2230. DOI: 10.1002/cbdv.200790180.
29. O'Reilly D.R., Howarth O.W., Rees H.H., Miller L.K. Structure of the ecdysone glucoside formed by a baculovirus ecdysteroid UDP-glucosyltransferase // Insect Biochem. 1991. Vol. 21. No 7. P. 795–801. DOI: 10.1016/0020-1790(91)90121-T.
30. O'Hanlon G.M., Howarth O.W., Rees H.H. Identification of ecdysone 25-O-β-D-glucopyranoside as a new metabolite of ecdysone in the nematode Parascaris equorum // Biochem. J. 1987. Vol. 248. No 1. P. 305–307. DOI: 10.1042/bj2480305.
31. Olennikov D.N. Phytoecdysteroids and flavonoids from Gastrolychnis tristis // Chem. Nat. Comp. 2018. Vol. 54. No 1. P. 204–206. DOI: 10.1007/s10600-018-2300-8.
Copyright (c) 2019 Khimiya Rastitel'nogo Syr'ya (Chemistry of plant raw material)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











