COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND FEATURES OF SURFACE MICROBIAL COMPLEXES OF LICHENS AND THEIR GROWTH SUBSTRATES
UDC 582.29;581.192;579.264
Abstract
The aim of the study was a comparative analysis of the chemical composition and features of the surface microbial complexes of three species of epigeic lichens (Cladonia rangiferina (L.), Cetraria islandica (L.), Peltigera horizontalis (Huds.)), one species of epiphytic lichen (Hypogymni aphysodes (L.) Nyl.) and their growth substrates.
It was found that the accumulation of inorganic ions by epigeic lichens exceeds their content in the soil by 4–450 times. Maximum biochemical mobility is characteristic of nutrients (potassium ions, phosphate ions). P. horizontalis and C. islandica were characterized by high biochemical mobility of copper and zinc, and H. physodes of cadmium and lead, and therefore these species of lichens can be considered bioaccumulators of these elements. The epiphytic lichen H. physodes was characterized by a relatively high content of phenolic compounds, which indicates its good antioxidant properties.
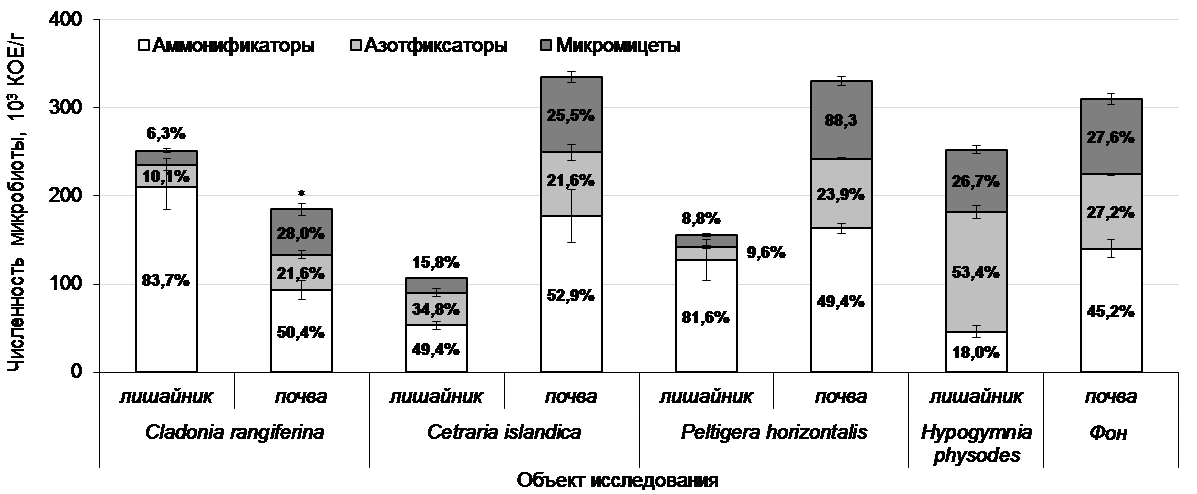
Different physiological groups made the maximum contribution to the structure of microbial populations on the surface of lichens. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria dominated in the microbial complex in the epiphytic lichen H. physodes, and ammonifiers in the epigeic lichens. There is a direct correlation between the number of ammonifiers and the total number of microorganisms on the surface of epigeic lichens and their number in the soil under lichens.
The gram-positive spore bacterium Bacillus polymyxa was isolated from the surface of the leafy lichen C. rangiferina (L.) into a pure culture, for which a high antagonistic activity was established with respect to phytopathogenic fungi pp. Fusarium and Alternaria. In the future, this strain can become the basis for the creation of an environmentally friendly biological product to combat plant diseases.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Golovko T.G., Shelyakin M.A., Pystina T.N. Teoreticheskaya i prikladnaya ekologiya, 2020, no. 1, pp. 6–13. DOI: 10.25750/1995-4301-2020-1-006-013. (in Russ.).
Provorov N.A., Tikhonovich I.A., Vorobiev N.I. Simbioz i simbiogenez. [Symbiosis and symbiogenesis]. St.-Petersburg, 2018, 464 p. (in Russ.).
Hyväuinen M., Härding R., Tuomi J. Oikos, 2002, vol. 98(3), pp. 498–504. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.980314.x.
Pankratov T.A. Microbiology, 2018, vol. 87, no. 1, pр. 79–88. DOI: 10.1134/S0026261718010149.
Korchikov Ye.S., Bolgov Ye.V., Il'ina Ye.S., Pankratov T.A. Samarskiy nauchnyy vestnik, 2018, vol. 7, no. 3 (24), pp. 59–64. (in Russ.).
Hale M.E. The biology of lichens. London, 1983, 192 p.
Ilyin V.B. Elementnyy khimicheskiy sostav rasteniy. [Elemental chemical composition of plants]. Novosibirsk, 1985, 130 p. (in Russ.).
Huneck S., Yoshimura I. Identification of lichen substances. Berlin, 1996, pp. 11–123. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-85243-5_2.
Podterob A.P. Pharm. Chem. J., 2008, vol. 42, pp. 582–588. DOI: 10.1007/s11094-009-0183-5.
Brovko O.S., Palamarchuk I.A., Sloboda A.A., Boytsova T.A., Gagushkina A.A., Val'chuk N.A. Uspekhi so-vremennogo yestestvoznaniya, 2016, no. 8, pp. 20–24. (in Russ.).
Knops J.M.H., Nash T.H., Boucher V.L., Schlesinger W.L. The Lichenologist, 1991, vol. 23, pp. 309–321. DOI: 10.1017/S0024282991000452.
Loppi S., Nelli L., Ancora S., Bargagli R. The Bryologist, 1997, vol. 100(2), pp. 251–253. DOI: 10.2307/3244059.
Nieboer E., Richardson D.H., Tomassini F.D. The Bryologist, 1978, vol. 81/2, pp. 226–246. DOI: 10.2307/3242185.
Herzig R., Liebendorfer L., Urech M., Ammann K., Guecheva W., Landolt M. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 1989, vol. 35, pp. 43–57. DOI: 10.1080/03067318908028377.
Loppi S., Frati L., Paoli L., Bigagli V., Rossetti C., Bruscoli C., Corsini A. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, vol. 326, pp. 113–122. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.12.003.
Domracheva L.I., Skugoreva S.G., Korotkikh A.I., Zabubenina Yu.S., Trefilova L.V., Kovina A.L., Domnina Ye.A., Timonov A.S. Teoreticheskaya i prikladnaya ekologiya, 2021, no. 2, pp. 183–188. DOI: 10.25750/1995-4301-2021-2-183-188. (in Russ.).
Kasimov N.S., Kosheleva N.Ye., Samonova O.A. Pochvovedeniye, 1995, no. 6, pp. 705–713. (in Russ.).
Sukhareva T.A. Trudy Karel'skogo nauchnogo tsentra RAN, 2016, no. 4, pp. 70–82. DOI: 10.17076/eco259. (in Russ.).
Bityutskiy N.P. Mikroelementy vysshikh rasteniy. [Microelements of higher plants]. St.-Petersburg, 2011, 368 p. (in Russ.).
Deyneko I.P., Deyneko I.V., Belov L.P. Khimiya rastitel'nogo syr'ya, 2007, no. 1, pp. 19–24. (in Russ.).
Palamarchuk I.A., Brovko O.S., Belyayev V.V., Bogolitsyn K.G., Boytsova T.A., Zhil'tsov D.V., Sloboda A.A., Val'chuk N.A. Khimiya rastitel'nogo syr'ya, 2018, no. 4, pp. 215–224. DOI: 10.14258/jcprm.2018043803. (in Russ.).
Kabata-Pendias A., Pendias H. Mikroelementy v pochvakh i rasteniyakh. [Trace elements in soils and plants]. Moscow, 1989, 439 p. (in Russ.).
Zhidkov A.N. Lesnoy vestnik, 2008, no. 1, pp. 151–156. (in Russ.).
Trifonova T.A., Salmin A.S. Yug Rossii: ekologiya, razvitiye, 2019, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 150–163. DOI: 10.18470/1992-1098-2019-2-150-163. (in Russ.).
Kasote D.M., Katyare S.S., Hegde M.V., Bae H. Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2015, vol. 11(8), pp. 982–991. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.12096.
Aoussar N., Rhallabi N., Mhand R.A., Manzali R., Bouksaim M., Douira A., Mellouki F. JMES, 2017, vol. 8(6), pp. 1968–1976.
Peltonen P., Vapaavuori E., Julkunen-Tiitto R. Global Change Biol., 2005, vol. 11(8), pp. 1305–1324. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.00979.x.
Golubkina N.A., Lapchenko V.A., Lapchenko Ye.V. Rastitel'nyye resursy, 2019, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 422–434. DOI: 10.1134/S0033994619030075. (in Russ.).
Medvedev S.S. Fiziologiya rasteniy. [Plant physiology]. St.-Petersburg, 2004, 336 p. (in Russ.).
Domracheva L.I., Kovina A.L., Ogorodnikova S.Yu., Korotkikh A.I., Korotkova A.V., Domnina Ye.A. Teoretich-eskaya i prikladnaya ekologiya, 2020, no. 1, pp. 130–135. DOI: 10.25750/1995-4301-2020-1-130-135. (in Russ.).
Korotkikh A.I., Zabubenina Yu.S., Domracheva L.I., Sheshegova T.K. Ekologiya rodnogo kraya: problemy i puti ikh resheniya: materialy XVI Vserossiyskoy nauchno-prakticheskoy s mezhdunarodnym uchastiyem konferentsii. [Ecology of the native land: problems and ways to solve them: materials of the XVI All-Russian scientific and practical confer-ence with international participation]. Kirov, 2021, vol. 2, pp. 26–29. (in Russ.).
Kratkiy opredelitel' bakteriy Bergi [Brief determinant of bacteria Bergi], ed. Dzh. Khoult. Moscow, 1980, 495 p. (in Russ.).
Copyright (c) 2022 chemistry of plant raw material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











