FLAVONOIDS OF POLYGONUM HETEROPHYLLUM LINDM.
Abstract
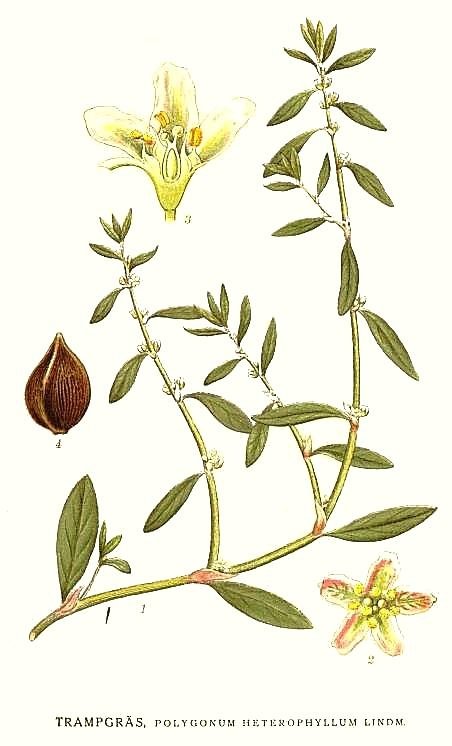
Species of the genus knotweed rich various biologically active substances - flavonoids, catechins, antrohoniny, stilbenes and others. Species of the genus knotweed characterized by high content of flavonoid compounds that have antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-allergic, anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory properties. The quantitative content and quality of the aerial part of flavonoids of Polygonum heterophyllum was studied. By the method of two-dimensional paper chromatography revealed that the extract of the aerial parts of the plant contains 11 compounds of polyphenol nature, 7 substances give a characteristic reaction to flavonoids. By preparative paper chromatography allocated two substances, by column chromatography on polyamide 3 substances in individual condition, 2 of them are aglycones, 3 of them are glycosides. On the basis of chromatographic data, spectral analyzes aglycones identified as quercetin and luteolin. According to the results of chromatography, spectral analyzes and acid hydrolyses glycosides identified as luteolin-7-glucoside, quercetin-3-glucoside, quercetin-3-galactoside and quercetin-3-arabinoside. It was found that depending on the habitat of plant flavonoid content varies between 1,44-2,12% on air-dry weight of raw materials.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Рзазаде Р.Я. Poд Polygonum L. Флора Азербайджана. Баку, 1954. Т. III. С. 166.
Wu X.Q. General review on chemical constituent and pharmacological effects of Radix Polygoni multiflori // LiShiZhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2009. Vol. 20. Pp. 146–147.
Xiaoxv Dong, Jing Fu, Xingbin Yin, Xuechun Li, Bo Wang, Sali Cao1, Jin Zhang, Hui Zhang, Yang Zhao, Jian Ni. Pharmacological and other Bioactivities of the Genus Polygonum // A Review. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Re-search. 2014. Vol. 13. N10. Pp.1749–1759
López S.N., Sierra M.G., Gattuso S.J., Furlàn R.L., Zacchino S.A. An unusual homoisoflavanone and a structurally-related dihydrochalcone from Polygonum ferrugineum (Polygonaceae) // Phytochemistry. 2006. N67. Pp. 2152–2158.
Datta B.K., Rahman M.M., Gray A.I., Sayed A.H., Auzi A.A., Sarke S.D. Polygosumic acid, a new cadinane sesquit-erpene from Polygonum viscosum, inhibits the growth of drug-resistant Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in-vitro // Journal of Natural Medicines. 2007. Vol. 61. Pp. 391–396.
Smolarz H.D., Potrzebowski M.J. Persilben – new carboxystilbene from Polygonum persicaria // J. Mol. Structure. 2002. Vol. 605. Pp.151–156
Qader S.W., Abdulla M.A., Chua L.S., Sirat H.M., Hamdan S. Pharmacological Mechanisms Underlying Gastro pro-tective Activities of the Fractions Obtained from Polygonum minus in Sprague Dawley Rats // Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012. Vol. 13. Pp. 1481–1496.
Kaul T.N., Middleton E. Jr., Ogra P.L. Antiviral effect of flavonoids on human viruses // J. Med. Virol. 1985. Vol. 15(1). Pp. 71–79.
Pandit S., Kim H.J., Park S.H., Jeon J.G. Enhancement of fluoride activity against Streptococcus mutans biofilms by a substance separated from Polygonum cuspidatum // Biofouling. 2012. Vol. 28. Pp. 279–287.
Hu B., An H.M., Shen K.P., Song H.Y., Deng S. Polygonum cuspidatum Extract Induces Anoikis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells Associated with Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Down regulation of Focal Adhesion Kinase // Evid-Based Compl. Alt. 2012. Pp. 1–9.
Kim H.N., Kim Y.R., Jang J.Y., Choi Y.W., Baek J.U., Hong J.W., Choi Y.H., Shin H.K., Choi B.T. Neuroprotective effects of Polygonum multiflorum extract against glutamateinduced ox-idative toxicity in HT22 hippocampal cells // J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013. Vol. 150. Pp. 108–115.
Cheong H., Ryu S.Y., Oak M.H., Cheon S.H., Yoo G.S., Kim K.M. Studies of structure activity relationship of flavonoids for the anti-allergic actions // Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998. Vol. 21(4). Pp.478–480.
Han J.H., Koh W., Lee H.J., Lee E.O., Lee S.J., Kim J.T., Khil J.H., Jeong S.J., Kim S.H. Analgesic and antiinflamma-tory effects of ethyl acetate fraction of Polygonum cuspidatum in experimental animals // Immunopharm. Immunot. 2012. Vol. 34. Pp. 191–195.
Jang H.G., Heo B.G., Park Y.S., Namiesnik J., Barasch D., Katrich E., Vearasilp K., Trakhtenberg S., Gorinstein S. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Anticancer Effects of the Seeds and Leaves of Indigo (Polygonum tinctorium Ait.) // Plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012. Vol. 167. Pp. 1986–2004.
Mabry T.S., Markham R.K., Thomson M.B. The systematic identification of flavonoids. Springer-Verlaq. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, 1970. 151 p.
Andersen O.M., Kenneth R. Markham. Flavonoids: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Applications. CRC Press, 2005. 1256 p.
Хайс И.М., Мацех К. Хроматография на бумаге. М., 1962. 851 c.
Федосеева Г.М., Мирович В.М., Переломова М.В. Фитохимический анализ растительного сырья, содержащего флавоноиды. Методическое пособие по фармакогнозии. Иркутск, 2009. 67 с.
Bryant E.T. A note of the differentiation between flavonoid glycosides and their aglycones // J. Amer. Pharm. Assoc. 1950. Vol. 39. N8. Pp. 480–488.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











