INFLUENCE OF THE NATURE AND CONCENTRATION OF EXTRACTANTS ON THE EXTRACTION OF FLAVO-NOIDS FROM THE CANADIAN GOLDENROD GRASS
Abstract
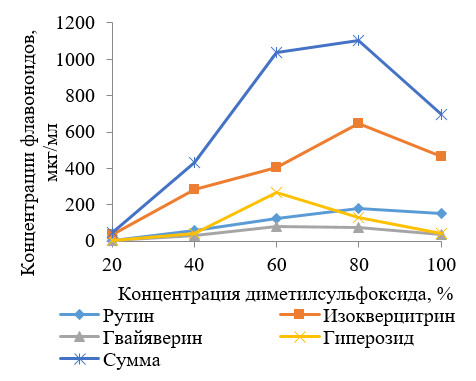
The paper presents the results of the study of influence of nature (in particular, dielectric constant and dynamic viscosity) and the concentration of the following extractants: methanol, ethanol, propanol, acetone, dimethylsulfoxide, ethyl acetate, propanol-2, butanol, butanol-2 for the extraction of flavonoids from Canadian goldenrod grass. The content of flavonoids in extracts prepared from the Canadian goldenrod grass was statistically significant (p<0.05) depending on the nature and concentration of the extractants used to prepare them. The most critical factor influencing on the extraction of this group of biologically active substances was the dynamic viscosity of the extractant. It was found that aqueous solutions of extractants have a greater extractive capacity than the corresponding absolute extractants. The maximum amount of flavonoids was extracted with use 80% methanol, 60% ethanol, 40% propanol, 60% acetone and 80% dimethylsulfoxide. From two to seven flavonoids were detected using the high-performance liquid chromatography method in the prepared extracts. The manner of the extraction of the flavonoids sum was predominantly determined by the dominant glycoside – isoquercitrin. Considering the better reproducibility of the extraction of the flavonoids sum, the wide application of ethanol and its aqueous solutions as extractants, the attribution of this extractant to low-toxic solvents and a greater extractive capacity for other classes of phenolic compounds (in particular, hydroxycinnamic acids), 60% ethanol is recommended to use for extraction of flavonoids from the Canadian goldenrod grass.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Карпова В.И., Гурина Н.С., Бузук Г.Н., Коноплева М.М., Любаковская Л.А., Кузьмичева Н.А., Кузнецова Н.П., Ловчиновский Ю.О. Флора Республики Беларусь: медицинское и хозяйственное значение: в 3 т. Т. 2. Витебск, 2004. 604 с.
Вторичный ареал: Золотая розга канадская, или Золотарник канадский Solidago сanadensis L. http://www.bookblack.ru/areal/17.htm. 22.11.2017.
Flora of New York. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Flora_of_New_York#Asterales. 22.11.2017.
Сулейманова Ф.Ш., Нестерова О.В., Матюшин А.А. Исторический опыт и перспективы использования травы золотарника канадского (Solidago сanadensis L.) в медицине // Здоровье и образование в XXI веке. 2017. Т. 19, №4. С.142–149.
Community herbal monograph on Solidago virgaurea L., Herba. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Community_herbal_monograph/2009/12/WC500018159.pdf. 22.11.2017.
Pharmacopee Française. – Paris, 1989. – 650 s.
Overview of comments received on «Community herbal monograph on Solidago virgaurea L., Herba» (EMEA/HMPC/285758/2007). http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Overview_of_comments_received_during_consultation/2009/12/WC500018158.pdf. 22.11.2017.
Assessment report on Solidago virgaurea L., Herba. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_HMPC_assessment_report/2009/12/WC500018161.pdf. 22.11.2017.
Schilcher H., Rau H. Nachweis der aquaretischen Wirkung von Birkenblätter und Gold-rutenauszügen im Tierversuch // Urologe. 1988. Vol. 28. S. 274–280.
Marksa M., Radusiene J., Jakstas V., Ivanauskas L., Marksiene R. Development of an HPLC post-column antioxidant assay for Solidago canadensis radical scavengers // Natura Product Research. 2016. Vol. 30, №5. P. 536–543.
Tao J.I.A.N.G., Bao–Kang H.U.A.N.G., Lu–Ping Q.I.N. A survey of chemical and pharmacological studies on Solidago // Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine. 2004. Vol. 4, №4. Р. 430–435.
British Pharmacopoeia. https://www.pharmacopoeia.com/. 09.08.2017.
Eurорeаn Рhаrmаcороeiа: EDQM. 9th Editiоn. http://www.edqm.eu/. 09.08.2017.
Apati P.G. Antioxidant constituents in Solidago canadensis L. and its traditional phytopharmaceuticals: thesis … Ph. D. Budapest, 2003. 19 p.
Савченко Л.Н., Маринина Т.Ф., Карпенко В.А. Получение экстракционного препарата противовоспалительного и мочегонного действия из травы золотарника канадского // Известия Самарского научного центра РАН. 2016. Т. 18, №2. С. 195–198.
Remil A., Chau-Chyun C. Solubility of Nutraceutical Compounds in Generally Recognized as Safe Solvents at 298 K // International Journal of Chemical Engineering and Applications. 2016. Vol. 7, №5. P. 289–294.
Chebil L., Humeau C., Anthoni J., Dehez F., Engasser J.-M., Ghoul M. Solubility of Flavonoids in Organic Solvents // Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 2007. Vol. 52, №5. P. 1552–1556.
Dixon D., Jeena G. Comparison of Different Solvents for Phytochemical Extraction Potential from Datura metel Plant Leaves // International Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2017. Vol. 1, №11. Р. 17–22.
Iloki-Assanga S.B., Lewis-Lujan L.M., Lara-Espinoza C.L., Gil-Salido A.A., Fernandez-Angulo D., Rubio-Pino J.L., Haines D.D. Solvent effects on phytochemical constituent profiles and antioxidant activities, using four different extraction formulations for analysis of Bucida buceras L. and Phoradendron californicum // BMC Res Notes. 2015. №8. Р. 396–409.
Ушанова В.М., Ушанов С.В., Ченцова Л.И. Влияние физических свойств растворителя на процесс экстракции коры хвойных пород // Вестник КраГАУ. 2009. №12. С. 210–214.
Производство лекарственных средств. Надлежащая практика выращивания, сбора, хранения лекарственного растительного сырья. ТКП 450-2012 (02041). Минск, 2013. – 14 с.
Zhang D.X. WHO guidelines on good agricultural and collections practices (GACP) for medicinal plants. Geneva, 2003. 72 p.
Равдель А.А., Пономарева А.М. Краткий справочник физико-химических величин. СПб, 2003. С. 112, 158–159.
Моисеев Д.В., Бузук Г.Н., Шелюто В.Л. Идентификация флавоноидов в растениях методом ВЭЖХ // Химико-фармацевтический журнал. 2011. Т. 45, №1. С. 35–38.
Лукашов Р.И. Факторы, влияющие на водно-спиртовую экстракцию флавоноидов из травы золотарника канадского // Рецепт. 2018. Т. 21, №1. С. 10–25.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











