VARIABILITY OF THE INDIVIDUAL-GROUP COMPOSITION OF POLYPHENOLS OF THE FRUITS AND LEAVES OF BLUE HONEYSUCKLE SAMPLES OF DIFFERENT ECOLOGICAL AND GEOGRAPHICAL ORIGIN IN THE OB FOREST-STEPPE
UDC 577.13:582.973:574.2:543.544.5.68.7
Abstract
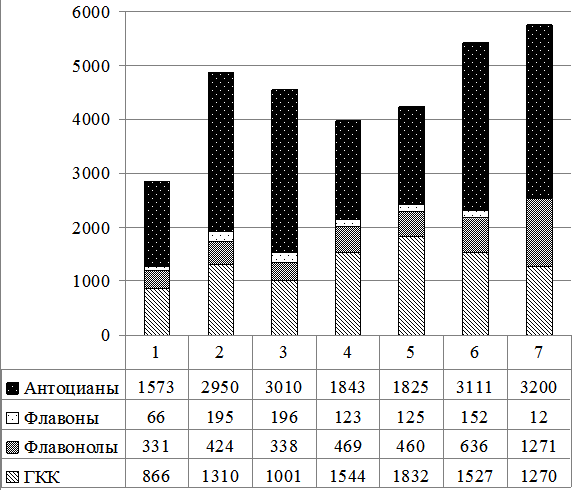
The aim of the study was to compare the variability of the composition, chemical identity and content of biologically active phenolic compounds in the fruits and leaves of the blue honeysuckle (Lonicera subsection Caeruleae) plants of different environmental and geographic provenances, sampled from the introduction plantation station in the forest steppe zone near the Ob River (Novosibirsk, Russia). In extracts from the leaves 25 individual compounds representing various polyphenolic classes were identified using HPLC-MS technique; seven of the compounds were identified as hydroxycinnamic acids, five compounds were flavonols, and eight compounds represented flavones. The maximal number of individual compounds was present in samples of the Altai subspecies of the tetraploid species L. caerulea subsp. altaica, whereas the minimal number was detected in samples of L. boczkarnikowae, a diploid species from the Russian Far East (Primorsky region). The lowest total polyphenolics content (6,260 mg/100 g of air-dry phytomass) was found in samples of L. caeruleae subsp. pallasii, whereas the content in samples from other blue honeysuckle subspecies ranged within 11.620-14.030 mg/100 g of air-dry phytomass. High content of flavones in extracts from leaves, always exceeding the flavonol content, was found to be a characteristic feature of L. caerulea subsp. altaica. Among L. сaerulea subspecies, L. сaerulea subsp. pallasii was shown to have the largest ratio of flavonols to flavones. L. boczkarnikowae also had high content of flavonols, significantly exceeding the flavones content in the plants organs. The main component of anthocyanins was cyanidin-3-glucoside, accounting for up to 91%. The fruits of L. caerulea subsp. altaica, L. сaerulea subsp. venulosa and L. boczkarnikowae had the highest anthocyanin content, ranging 2.950–3.200 mg/100 g air-dry phytomass, whereas the fruits of L. сaerulea subsp. pallasii had the lowest one (1,573 mg/100g). Extracts from the leaves were found to have significantly higher polyphenolics content as compared to the ones from the fruits; thus the leaves can be recommended as a prospective medicinal source.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Plekhanova M.N. Trudy po prikladnoy botanike, genetike i selektsii, 2006, vol. 162, pp. 59–69. (in Russ.).
Gidzyuk I.K. Zhimolost' so s"yedobnymi plodami. [Honeysuckle with edible fruits]. Tomsk, 1981, 168 p. (in Russ.).
Huo J.-W., Yang G.-H., Sui W., Yu Z.-Y. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2005, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 159–164.
Fu L., Okamoto H., Hoshino Y., Esaki Y., Kataoka T., Shibata Y. Engineering in Agriculture, 2011, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 12–17. DOI: 10.1016/S1881-8366(11)80003-0.
Petrova V.P. Dikorastushchiye plody i yagody. [Wild fruits and berries]. Moscow, 1987, 248 p. (in Russ.).
Rastitel'nyye resursy SSSR. Tsvetkovyye rasteniya, ikh khimicheskiy sostav, ispol'zovaniye: Caprifoliaceae – Plantagi-naceae. [Plant resources of the USSR. Flowering plants, their chemical composition, use: Caprifoliaceae – Plantagina-ceae]. Leningrad, 1990, 328 p. (in Russ.).
Thompson M.M. Journal of the American Pomological Society, 2006, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 164–168.
Lefol E. Haskap market development – the Japanese opportunity. University of Saskatchewan, 2007, 53 p.
Rupasinghe H.P.V., Yu L.J., Bhullar K.S., Bors B. Can. J. Plant Sci., 2012, vol. 92, pp. 1311–1317. DOI: 10.4141/CJPS2012-073.
Apak R., Gorinstein S., Böhm V., Schaich K.M., Özyürek M., Güçlü K. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2013, vol. 85, no. 5, pp. 957–998. DOI: 10.1351/PAC-REP-12-07-15.
Wu S., Yano S., Chen J., Hisanaga A., Sakao K., He X., Hou D.-X. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, vol. 65, no. 25, pp. 5133–5141. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01599.
Minami M., Nakamura M., Makino T. Hindawi Bio Med Research International, 2019, vol. 2019, 1797930, 12 p. DOI: 10.1155/2019/1797930.
Rupasinghe H.P.V., Boehm M., Sekhon-Loodu S., Parmar I., Bors B., Jamieson A. Biomolecules, 2015, vol. 5, pp. 1079–1098. DOI: 10.3390/biom5021079.
Rupasinghe H.P.V., Arumuggam N., Amararathna M., De Silva A.B.K.H. J. Funct. Foods, 2018, vol. 44, pp. 24–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.02.023.
De Silva A.B.K.H., Rupasinghe H.P.V. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2020, vol. 88, 103402. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103452.
Strel'tsina S.A., Sorokin A.A., Plekhanova M.N., Lobanova Ye.V. Agrarnaya Rossiya, 2006, no. 6, pp. 67–72. (in Russ.).
Boyarskikh I.G., Yushkova Yu.V., Chernyak Ye.I., Morozov S.V. Vestnik Altayskogo gosudarstvennogo agrarnogo universiteta, 2011, no. 3, pp. 39–46. (in Russ.).
Auzanneau N., Weber P., Kosińska-Cagnazzo A., Andlauer W. J. Food Compos. Anal., 2018, vol. 66, pp. 81–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.12.006.
Senica M., Stampar F., Mikulic-Petkovsek M. Scientia Horticulturae, 2018, vol. 238, pp. 215–221. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.04.056.
Kaczmarska E., Gawroński J., Dyduch-Sieminska M., Najda A., Marecki W., Zebrowska J. Turk. J. Agric. For., 2015, vol. 39, pp. 394–402. DOI: 10.3906/tar-1404-149.
Kucharska A.Z., Sokół-Łetowska A., Oszmianski J., Piórecki N., Fecka I. Molecules, 2017, vol. 22, no. 3, 405. DOI: 10.3390/molecules22030405.
Thompson M.M., Barney D.L. Journal of the American Pomological Society, 2007, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 25–33.
Bors B., Thomson J., Sawchuk E., Reimer P., Sawatzky R., Sander T. Haskap breeding and production – final report. Saskatchewan Agriculture: Regina. Saskatchewan, Canada, 2012, 145 p.
Boyarskikh I.G., Vasil'yev V.G., Kukushkina T.A. Rast. resursy, 2014, vol. 1, pp. 105–121. (in Russ.).
Boyarskikh I.G., Syso A.I., Vasil'yev V.G., Siromlya T.I. Rast. resursy, 2016, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 135–150. (in Russ.).
Harborne J.B., Williams C.A. Phytochemistry, 2000, vol. 55, pp. 481–504.
Karak P. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. & Res., 2019, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 1567–1574. DOI: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(4).1567-74.
Michalak A. Pol. J. Environ. Stud., 2006, vol. 15, pp. 523–530.
Zidorn C. Phytochem Rev., 2010, no. 9, pp. 197–203. DOI: 10.1007/s11101-009-9143-7.
Agati G., Azzarello E., Pollastri S., Tattini M. Plant Science, 2012, vol. 196, pp. 67–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.07.014.
Kumar S., Pandey A.K. The Scientific World Journal, 2013, vol. 2013, 162750, 16 p. DOI: 10.1155/2013/162750.
Boyarskikh I.G., Syso A.I., Siromlya T.I. Sibirskiy ekologicheskiy zhurnal, 2019, no. 6, pp. 727–741. DOI: 10.15372/SEJ20190608. (in Russ.). [Boyarskiha I.G., Syso A.I., Siromlya T.I. Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 2019, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 594–606. DOI: 10.1134/S1995425519060039].
Brunetti C., Fini A., Sebastiani F., Gori A., Tattini M. Front. Plant Sci., 2018, vol. 9, 1042. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01042.
Khramova Ye.P. Khimiya rastitel'nogo syr'ya, 2014, no. 1, pp. 185–193. DOI: 10.14258/jcprm.1401185. (in Russ.).
Copyright (c) 2021 chemistry of plant raw material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors, which are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. Authors retain the copyright to the work and transfer to the journal the right of the first publication along with the work, at the same time licensing it under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which allows others to distribute this work with the obligatory indication of the authorship of this work and a link to the original publication in this journal .
2. The authors retain the right to enter into separate, additional contractual agreements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published by this journal (for example, to place it in the university depository or to publish it in a book), with reference to the original publication in this journal.
3. Authors are allowed to post their work on the Internet (for example, in a university repository or on their personal website) before and during the review process of this journal, as this may lead to a productive discussion, as well as more links to this published work.











